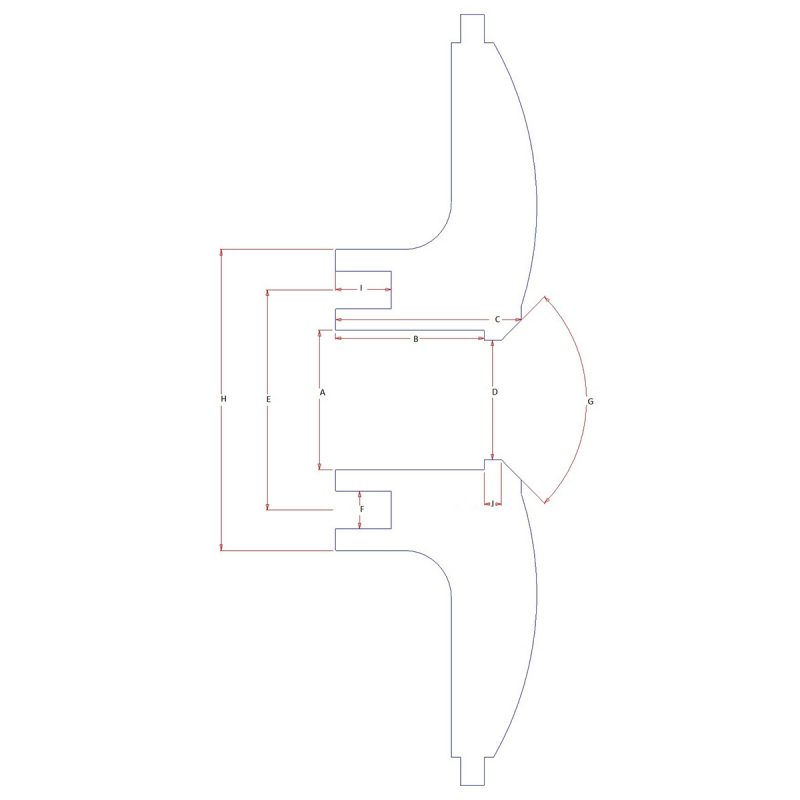
Dimensions and Measurement Instructions
Correct Measurement Method
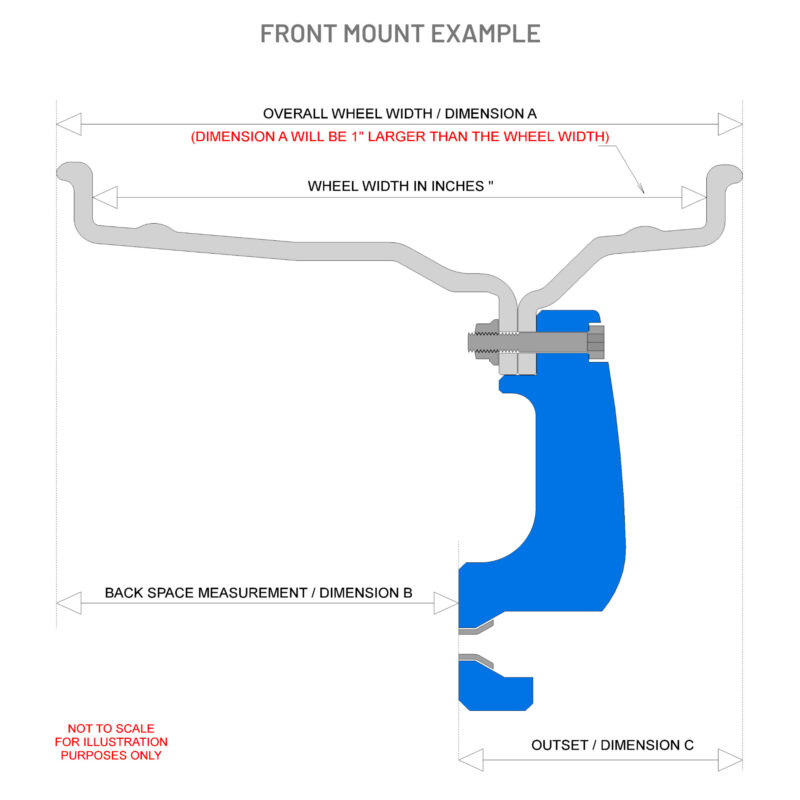
Dimension “A” is total width of the wheel (edge to edge) this is 1.0″ wider than the actual wheel size (tyre bead to tyre bead).
For example if you are ordering an 8.0″ X 15″ wheel (tyre bead to tyre bead) Dimension “A” will be 9.0″ (edge to edge).
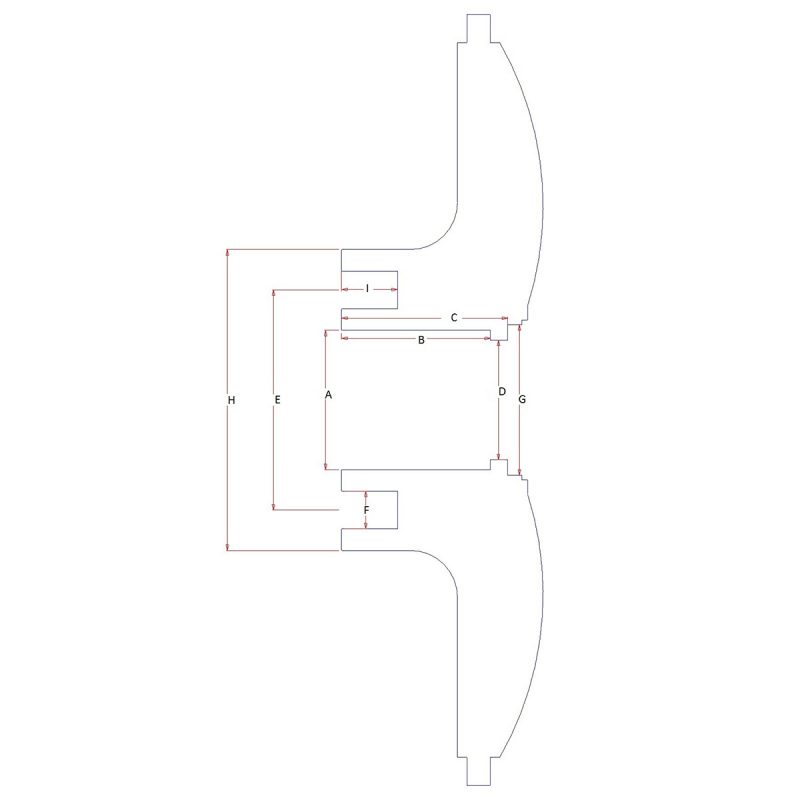
‘A’ = TOTAL WIDTH OF WHEEL
‘B’ = BOLT UP FACE INTO CAR
‘C’ = BOLT UP FACE TO INNER EDGE OF WING
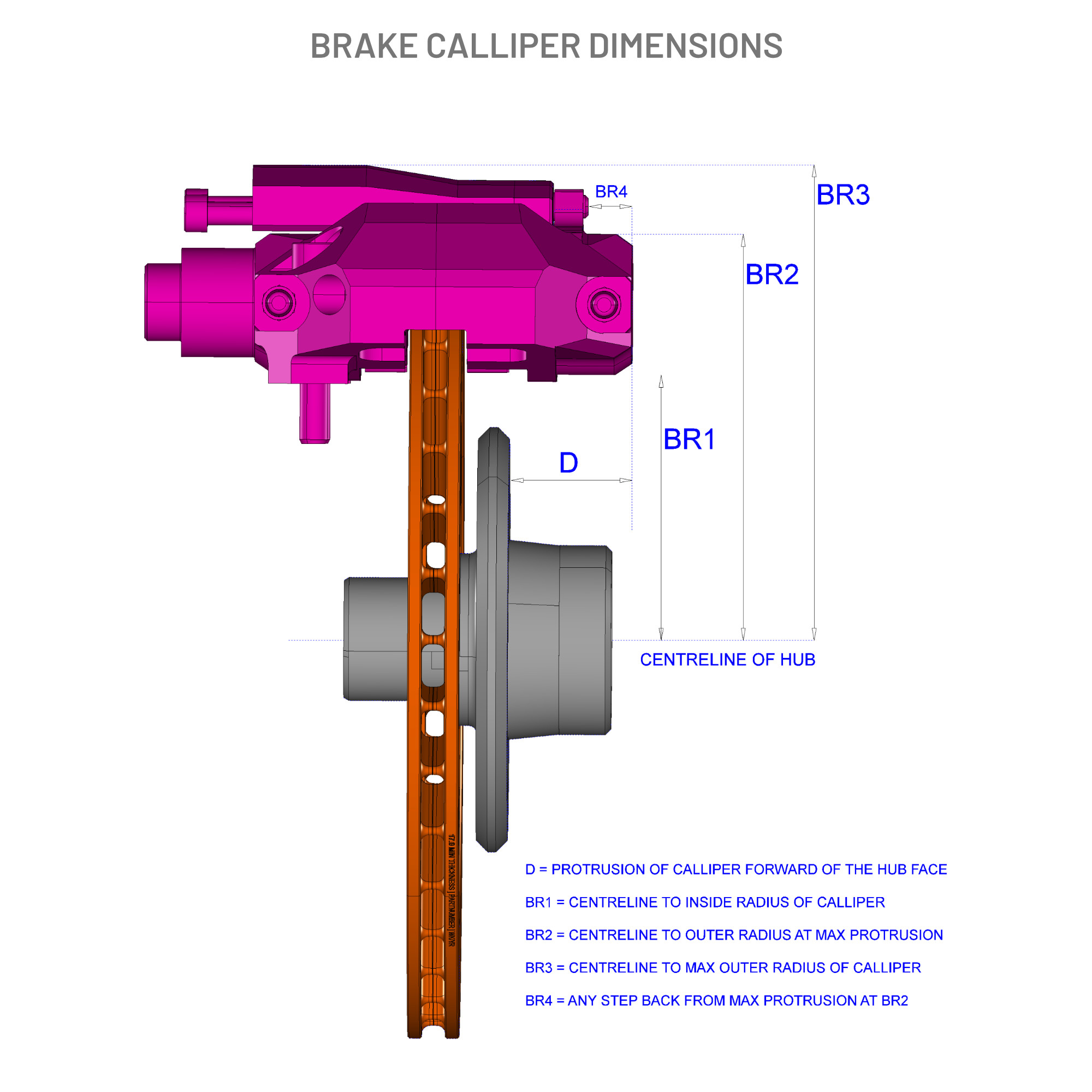
‘D’ = FORWARD PROTRUSION OF BRAKE CALIPER
Three piece wheels consist of a CNC formed inner and outer rim section and a centre hub. When selecting your wheel size it is important to remember that our wheel sizes given are tyre seat to tyre seat.
EXAMPLE: IF YOU ORDER A 7.0 x 15” WHEEL DIMENSION ‘A’ = 8.0”
Offset
The amount of wheel going INTO the car from the wheel centreline is POSITIVE.
The amount of wheel moving OUT of the car from the centreline is NEGATIVE.
The measurement diagram shows a POSITIVE offset, along with dimensions ‘A’ ‘B’ ‘C’ and ‘D’. The measurement from the wheel mounting face to the outside of the car STATE C DIMENSION. The measurement to check the brake caliper protrusion forwards of the wheel mounting face STATE D DIMENSION.
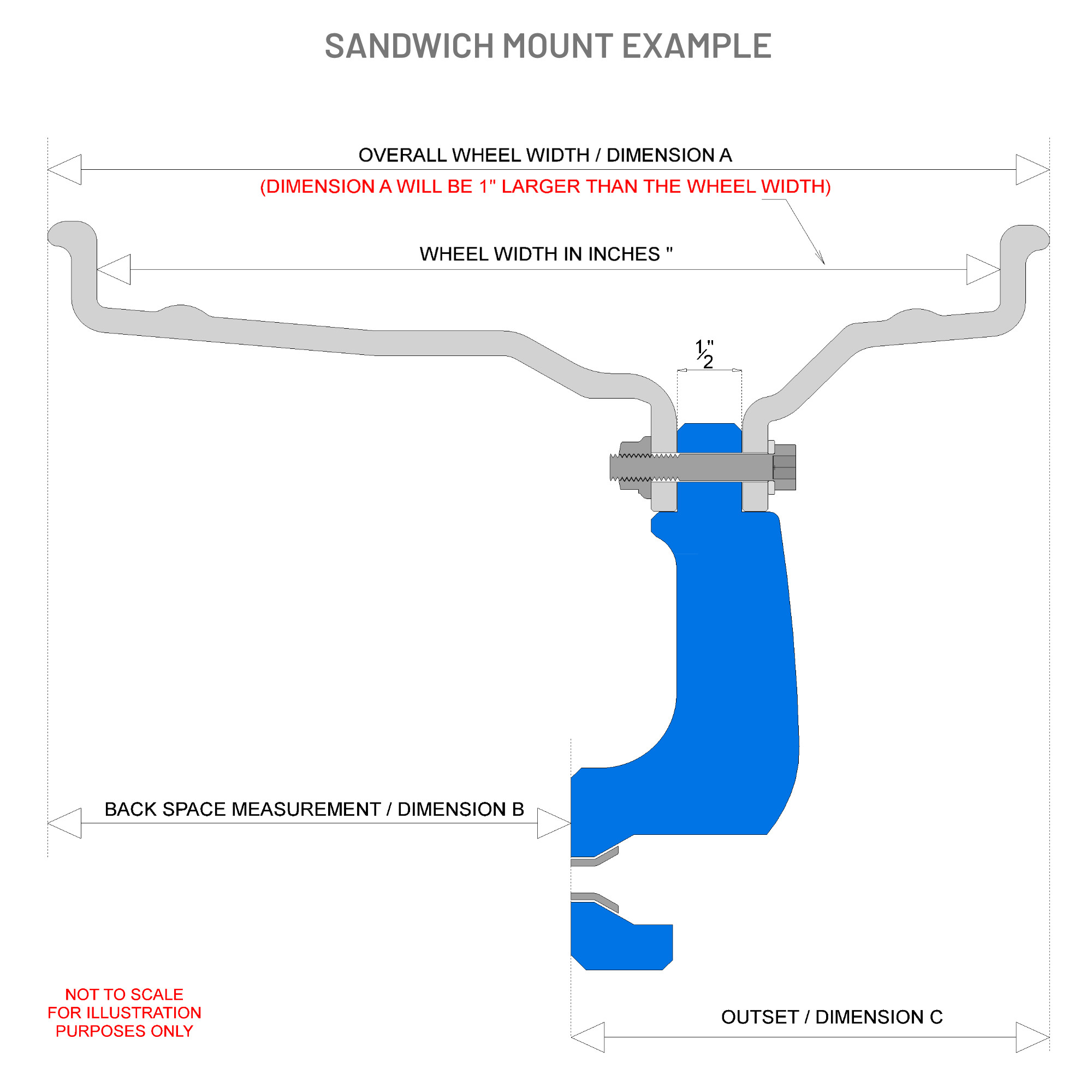
Split Rim Wheels
A split rim wheel is made up of three key components: the outer rim, centre hub, and inner rim. Depending on the required fitment, these parts can be assembled in one of two configurations: Front Mount or Sandwich Mount construction.
For a more traditional look, we also offer a Classic Build option—available with Front Mount construction only—where the perimeter bolts are hidden for a cleaner, more understated appearance.
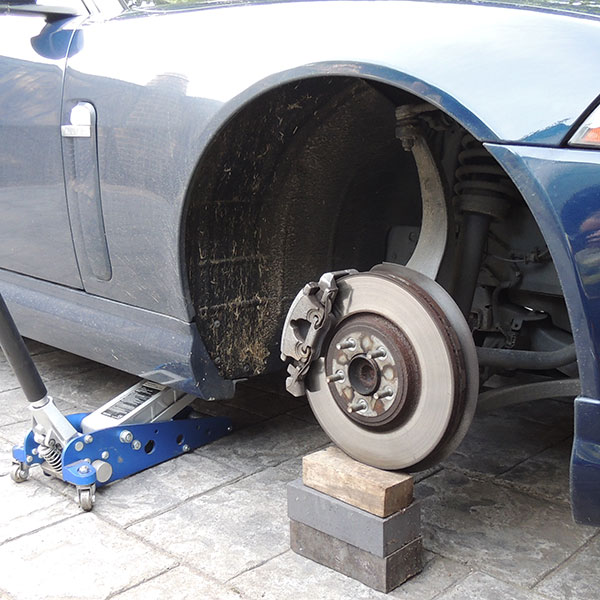
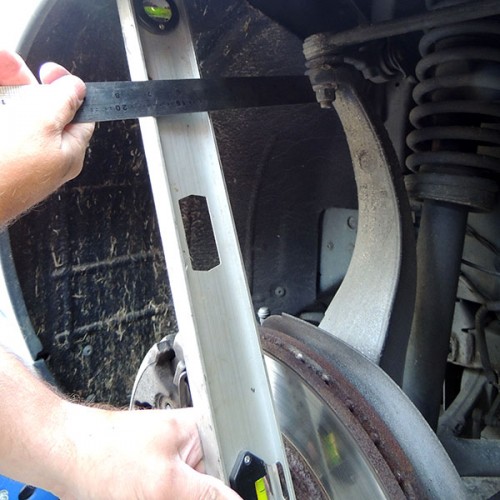
Step 2, Measuring Dimension B
Use a straight edge (steel rule or spirit level) and place it against it the hub face on the car running vertical from top to bottom (photo measurement B-1).
Then with a steel rule (best) or tape measure, measure the distance from the back edge of your straight edge (photo measurement B-A) – to the first fouling point a wheel would come into contact with, this usually the shock absorber or spring/upright (photo measurement B-B).
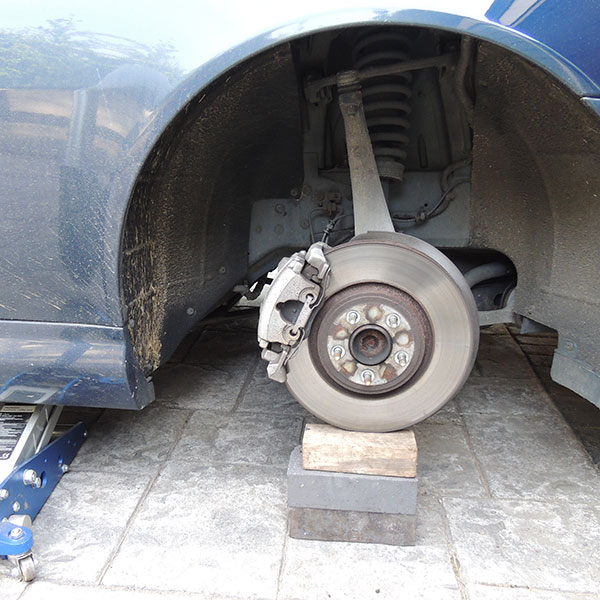
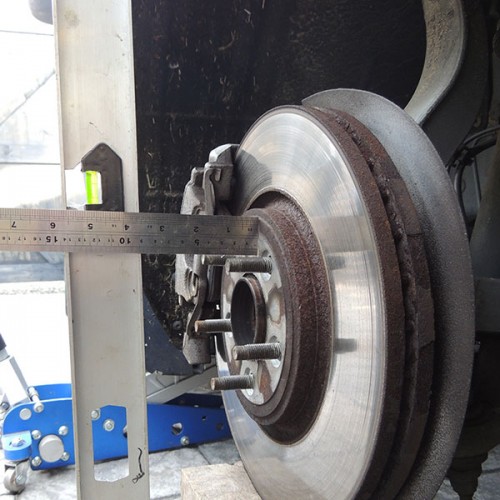
Step 3, Measuring Dimension C
Using a spirit level place it against the car in the centre of the wheel arch in a vertical position and ensure it straight (90 deg to the floor) and touching the bodyline of the car, then measure back to the hub face on the car from the straight edge, you can also use a plumb line hung from the centre of the wheel arch, (photos measurement C and measurement C-A).
Measure the thickness of the wheel arch edge with a steel rule/tape measure as shown, (photo Arch Width).
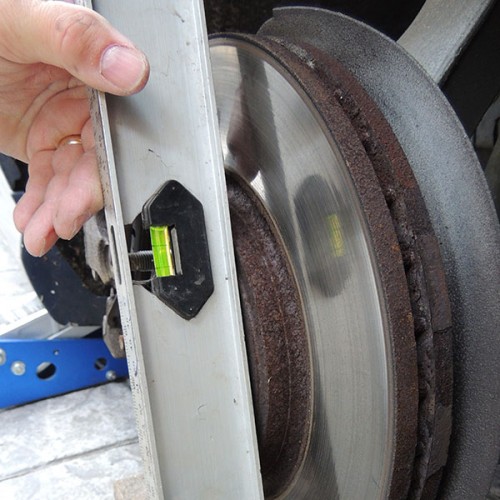
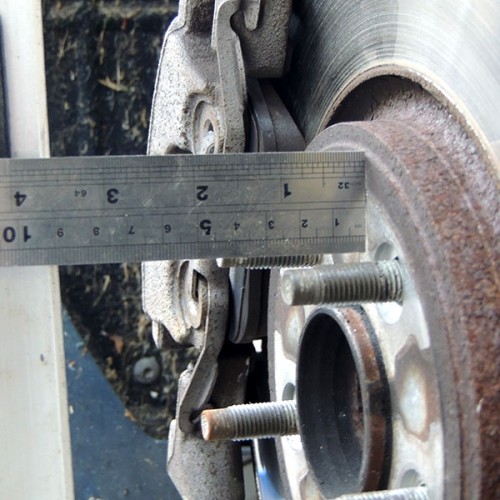
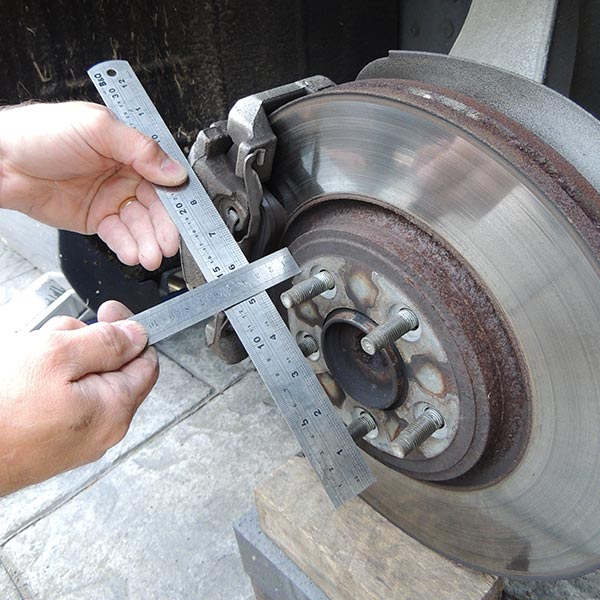
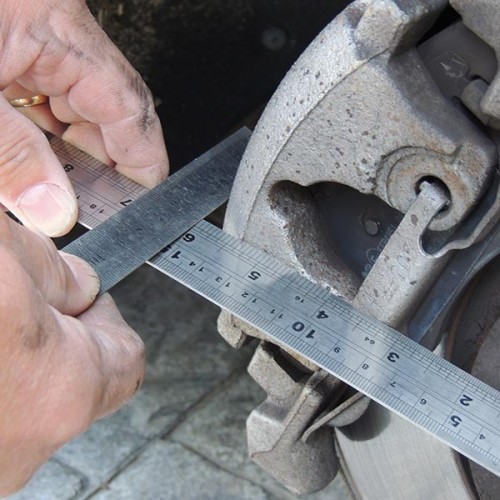
Brake Calliper Radius
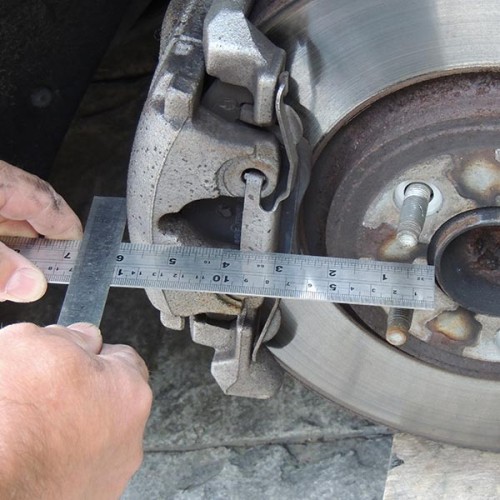
A measurement we sometimes require is the brake calliper radius, to measure this place a straight edge against the outside edge of the calliper at the furthest point from the centre of the hub, (photo Calliper Radius – Full).
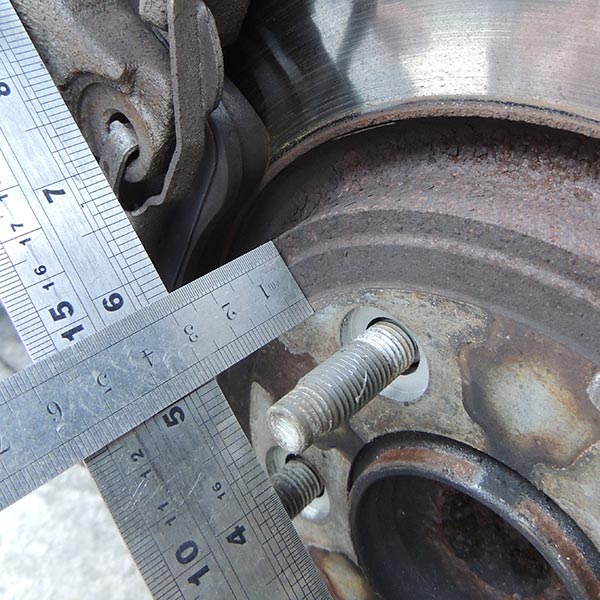
Take a steel rule and place it across the face of the calliper so it meets the edge of the hub location in the centre of the hub (photo Calliper Radius – 1).
Where the rule meets the straight edge will give you the radius of the brake calliper (photo Calliper Radius – 2).
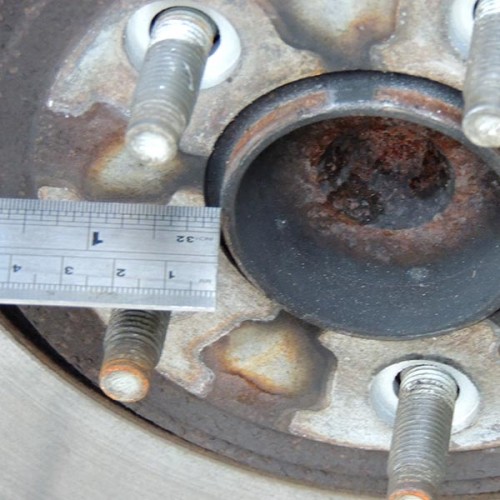
PCD (Pitch Circle Diamater)
Pitch Circle Diameter stud patterns
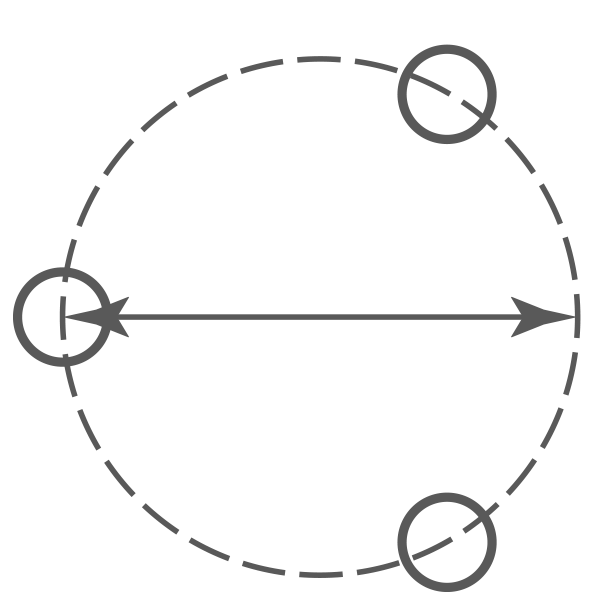
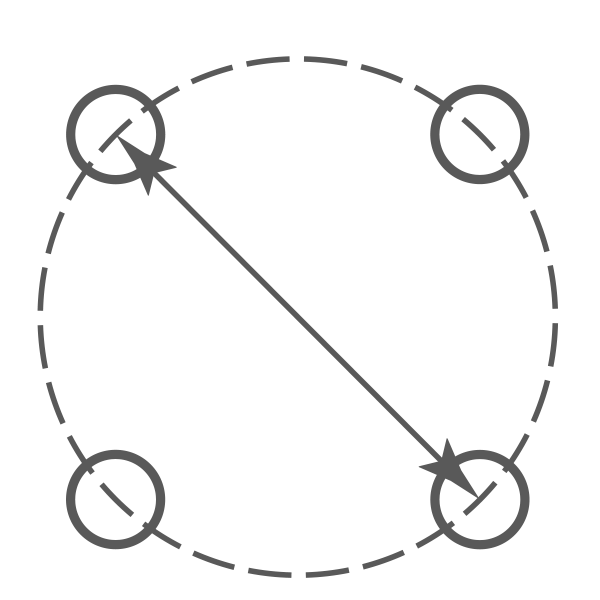
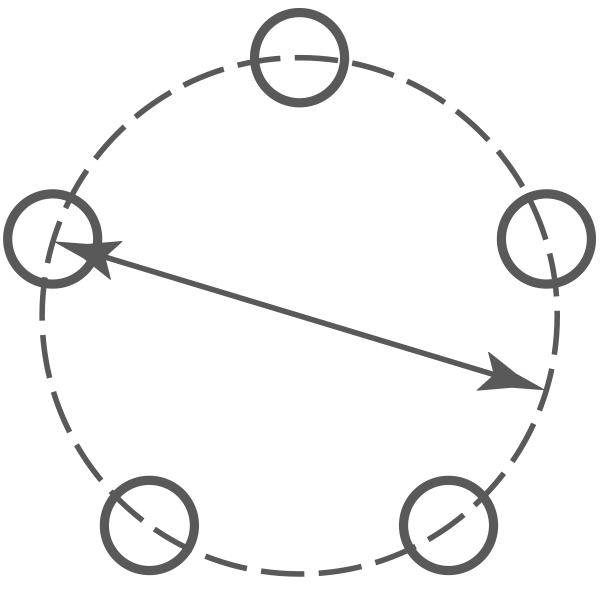
We can accommodate larger PCD sizes on our Billet centres. Example 5x130mm plus. We can also do CENTRE LOCK in some Cast and Billet styles.
If you require further information on any of the above, please give us a call and we will be happy to help.